Insurance, for example, is usuallypurchased for more than one month at a time (six months typically).The company does not use all six months of the insurance at once,it uses it one month at a time. As each month passes, the company will adjustits records to reflect the cost of one month of insuranceusage. We begin with the left side of the equation, the assets,and work toward the right side of the equation to liabilities andequity. A business can now use this equation to analyze transactions inmore detail. But first, it may help to examine the many accountsthat can fall under each of the main categories of Assets,Liabilities, and Equity, in terms of their relationship to theexpanded accounting equation. Essentially, the expanded accounting equation is derived from the basic accounting equation.
What Is the Expanded Accounting Equation?
Essentially, anything acompany owes and has yet to pay within a period is considered aliability, such as salaries, utilities, and taxes. — At the beginning of the year, Corporation X was formed and 1,000, $10 par value stocks were issued. X receives the cash from the new shareholders and also grants them equity in the company.
- The second shows how much money the owners took out of the company.
- More specifically, this extended equation highlights the particular relationship between the balance sheet and the company’s net income.
- Accounts payable recognizes that the company owes money and hasnot paid.
- If you find it difficult, you may refer back to the explanation in the previous lesson.
- — At the end of the year, X ends up with large profits and the management decides to issue dividends to its shareholders.
Learning Outcomes
A business can now use this equation to analyze transactions in more detail. But first, it may help to examine the many accounts that can fall under each of the main categories of Assets, Liabilities, and Equity, in terms of their relationship to the expanded accounting equation. We can begin this discussion by looking at the chart of accounts.
What Is The Expanded Accounting Equation
This means that revenues exceeded expenses for the period, thus increasing retained earnings. If a business has net loss for the period, this decreases retained earnings for the period. This means that the expenses exceeded the revenues for the period, thus decreasing retained earnings. The increases small business advertising and marketing costs may be tax deductible (credits) to common stock and revenues increase equity; whereas the increases (debits) to dividends and expenses decrease equity. Remember, the normal balance of each account (asset, liability, common stock, dividends, revenue, or expense) refers to the side where increases are recorded.
Income Statement and Balance Sheet
First, however, in Define and Examine the Initial Steps in the Accounting Cycle we look at how the role of identifying and analyzing transactions fits into the continuous process known as the accounting cycle. These retained earnings are what the company holds onto at the end of a period to reinvest in the business, after any distributions to ownership occur. Stated more technically, retained earnings are a company’s cumulative earnings since the creation of the company minus any dividends that it has declared or paid since its creation.
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone.
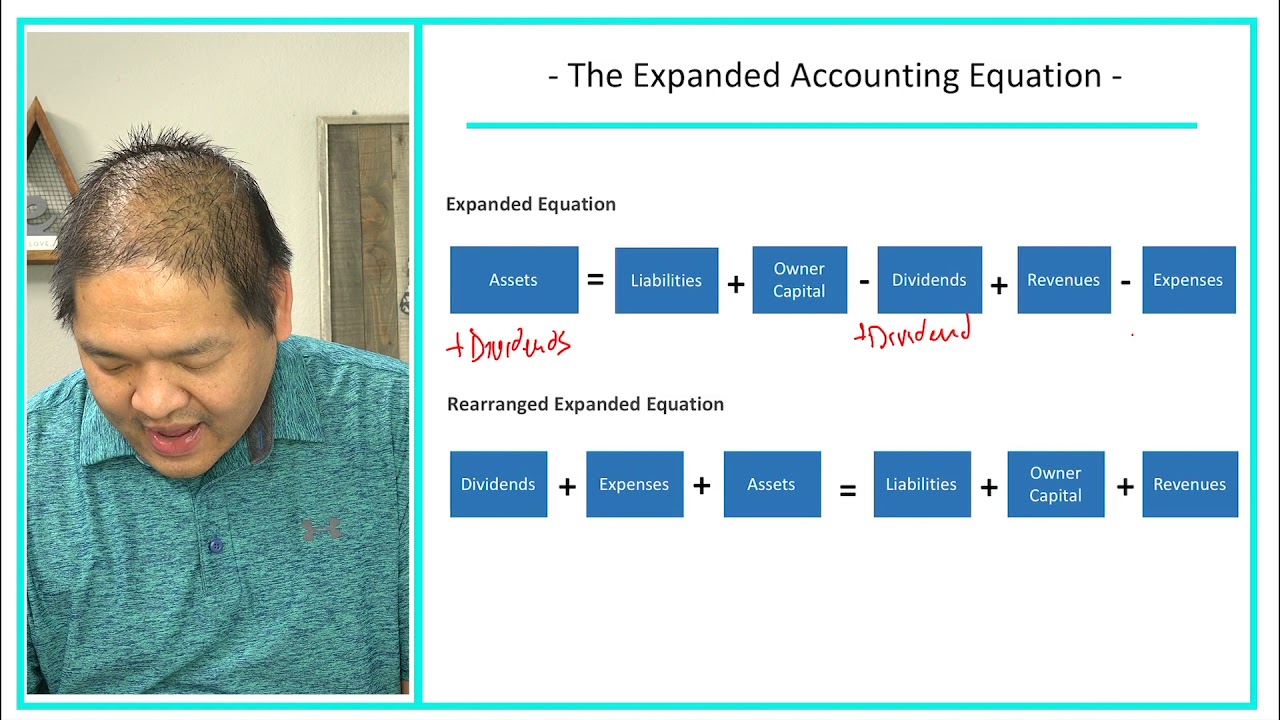
If you take the total of the right side of the equation (i.e. liabilities, capital contribution, income, expense, and withdrawals) you will get $36,450, which is equal to the total assets in the left side. Notice that all of the equations’ assets and liabilities remain the same—only the ownership accounts are changed. Here is the expanded accounting equation for a sole proprietorship. Revenue and expenses (or net income) provide the impact of the company’s operating revenue and expenses on the stockholder equity.
It is an important concept from the accounting point of view because it provides a picture of the organization’s financial well-being. The accounting equation includes information from the balance sheet and provides information about the income-expenditure statement. Accounts payable recognizes that the company owes money and hasnot paid.
In the case of stockholder equity, the draws to cover salaries take the form of dividends paid out by investors. The expanded equation highlights where and how these draws decrease overall equity. The owner’s investments in the business typically come in theform of common stock and are called contributedcapital. There is a hybrid owner’s investment labeled aspreferred stock that is a combination of debt and equity (a conceptcovered in more advanced accounting courses). The company willissue shares of common stock to represent stockholder ownership.You will learn more about common stock in Corporation Accounting. As you can see with this example, the basic accounting equation remains balanced although we’ve split the stockholders’ equity into its components.

As seen in the example above, the net result of the expanded accounting equation is such that the corporation’s assets are equal to the net impact of stockholder equity, liabilities, and net earnings. A balanced equation also ensures that the whole accounting process has been followed properly. It further helps strengthen the fact that all the debit and credit entries about all transactions entered during the period have been considered. Contributed capital and dividends show the effect of transactions with the stockholders.

 تا سه برابر شارژ هدیه بگیرید
تا سه برابر شارژ هدیه بگیرید